Client Overview: City of Los Angeles
- Client: Los Angeles Bureau of Street Lighting (Department of Public Works, City of Los Angeles)
- Location: Los Angeles, California
- Population: 4 Million (10 Million, including surrounding area)
- EVs on the road: 278,2631 (Los Angeles County)
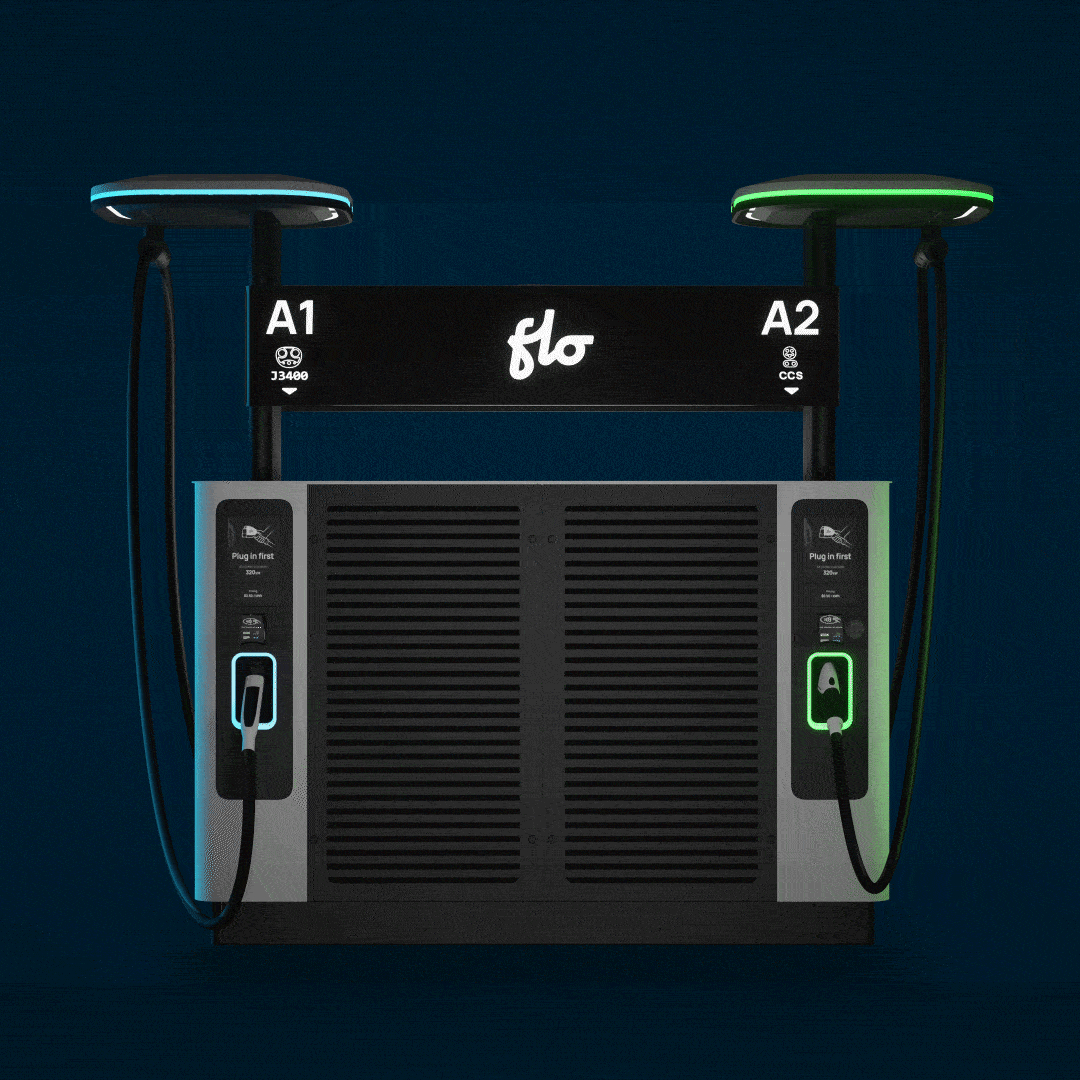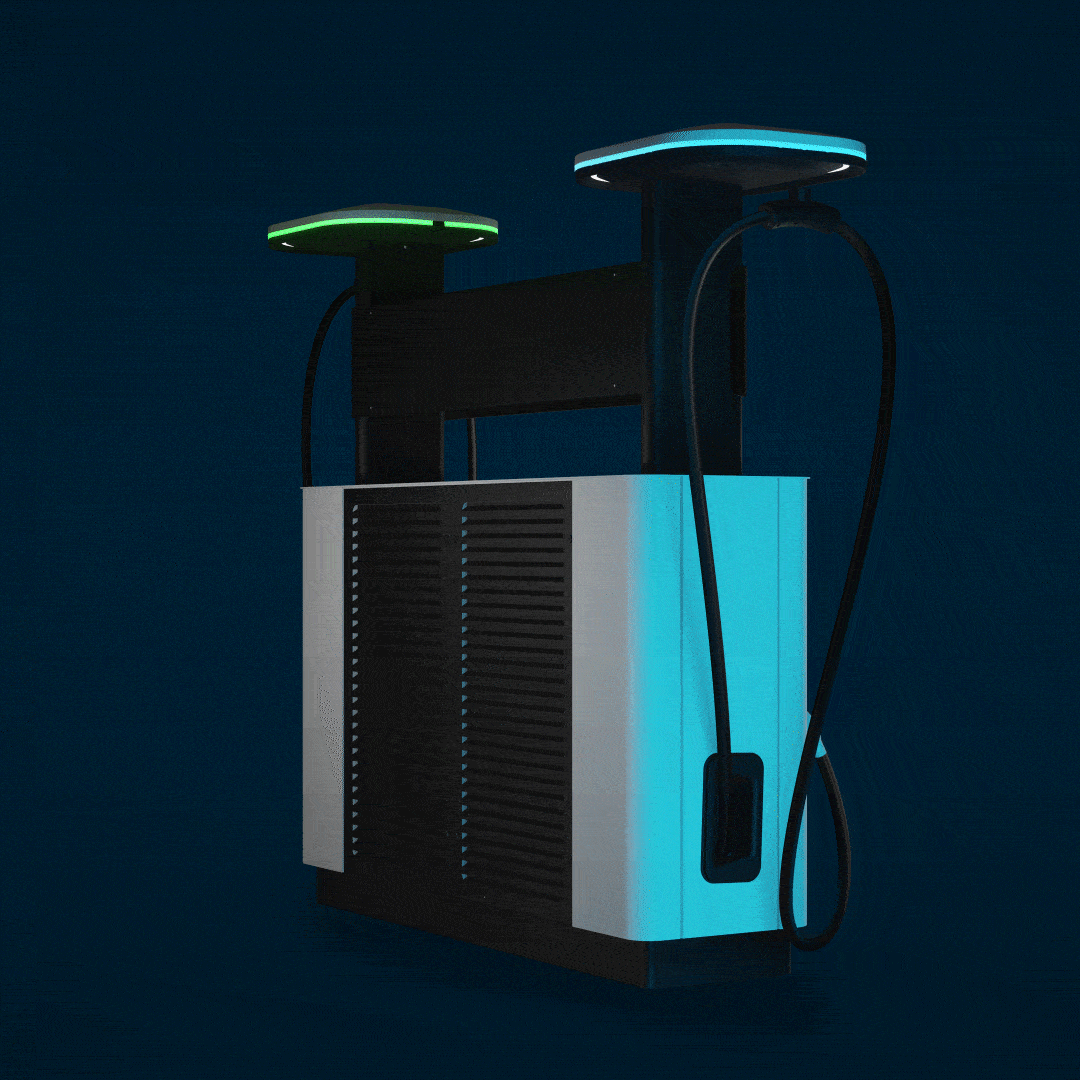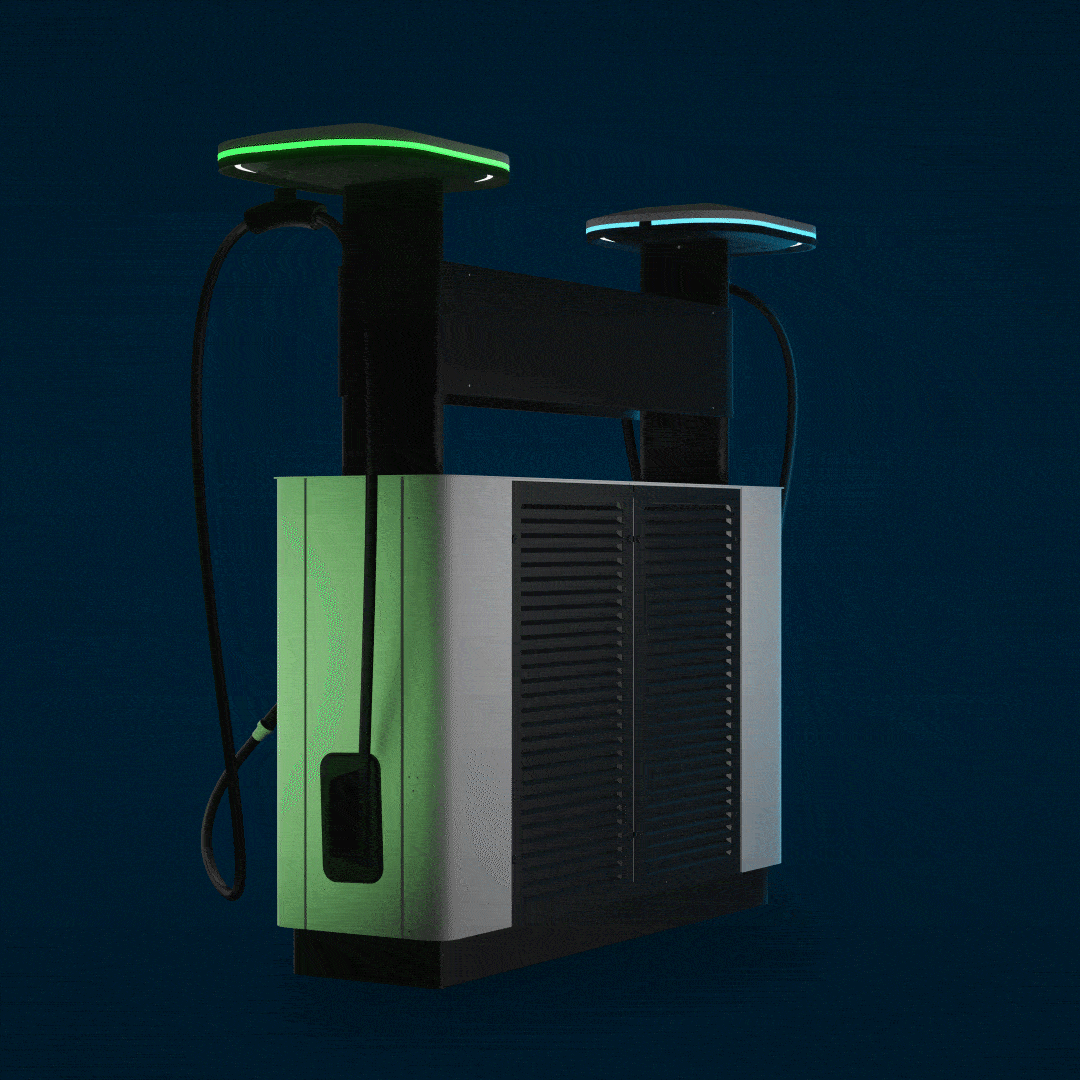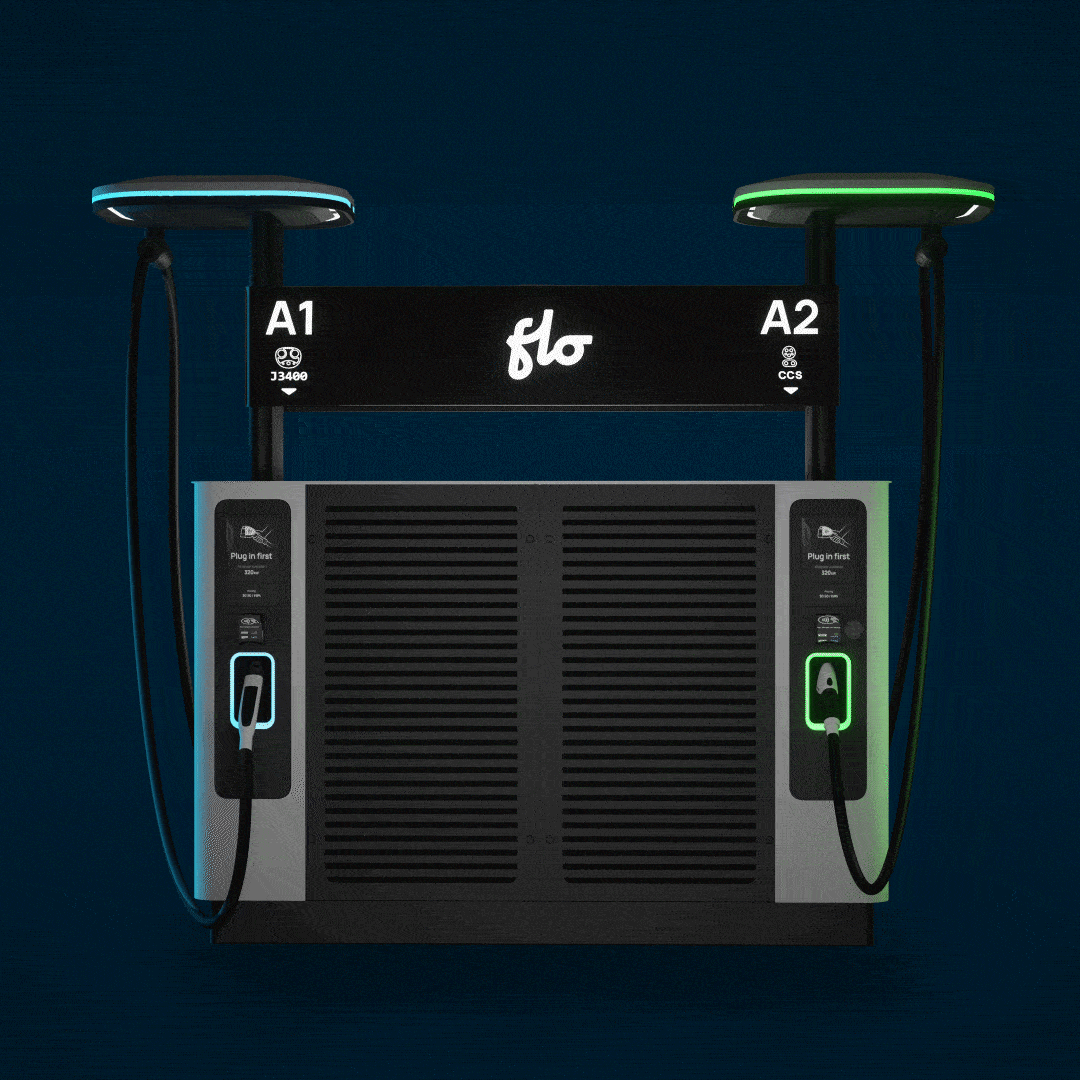
- Station models: SmartTWO™
- Project goals: Leverage Existing Infrastructure Condense Deployment Timeline Achieve large geographical exposure Foster EV Adoption
The City of Los Angeles is one of the largest metropolitan centers in America, with a population of approximately 10 million people when including surrounding counties. With a population of this size and a large geographical area to navigate, it is easy to understand that approximately 84% of the city’s population relies on personal vehicles to get around2. A driving populace of this size is bound to produce a significant amount of greenhouse gasses, and in fact almost 33% of the Los Angeles’ greenhouse gas emissions are from combustion vehicles (cars and trucks)3. Correspondingly, Los Angeles’ air routinely ranks among the nation’s most polluted; however, the city is taking pronounced steps to combat the rise of greenhouse gas emissions. As part of their “Green New Deal”, the city of Los Angeles has committed to transitioning to a more sustainable model of transportation in the immediate future, and the city’s Department of Public Works has partnered with electric vehicle charging manufacturer FLO to install Level 2 charging stations at various locations through the city’s sizeable urban sprawl.
FLO’s partner for this project was the Los Angeles Bureau of Street Lighting (LABSL), who oversees the city’s complex lighting infrastructure featuring over 220,000 individual lighting poles.
A recent system upgrade saw the department transition to an LED energy system, which resulted in excess available power inside the lighting infrastructure. As part of their commitment
to fostering EV adoption inside the city’s limits, the city of Los Angeles aspired to using this excess power to install EV charging infrastructure and combat “range anxiety.
In detailing their vision for the project, LABSL articulated a specific set of goals and a unique series of challenges. Early conversations with the utility revealed their intentions for the project to be threefold:
- First, to leverage the department’s existing infrastructure (street lighting poles) for installation, thus reducing the overall cost and timeline for deployment,
- Second, to source robust and durable hardware capable of functioning in all the diverse neighborhoods the city of Los Angeles offers,
- And finally, to deploy the charging stations in a way that would cover a large geographical range, while servicing the largest percentage of the EV driving community possible.
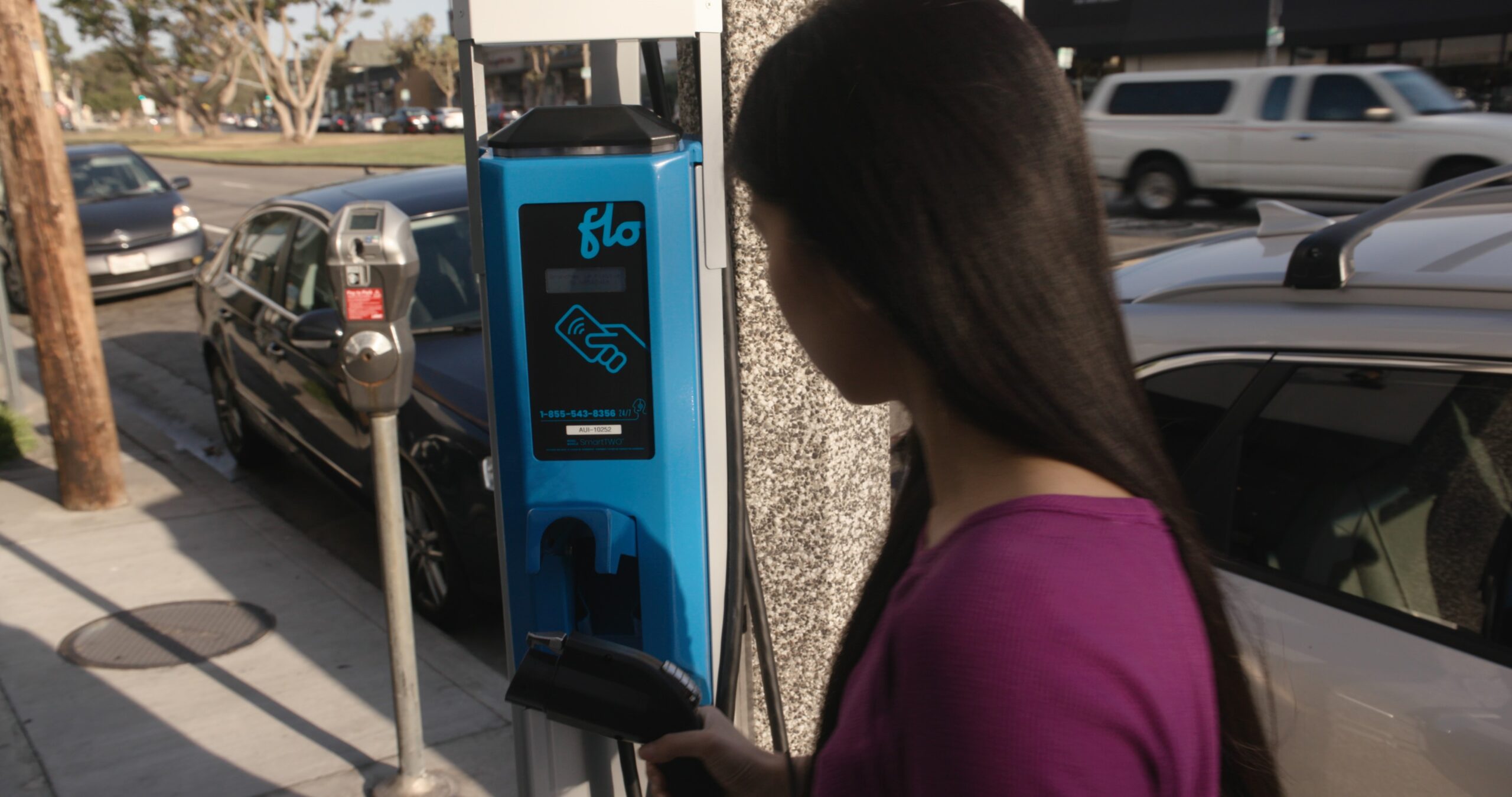
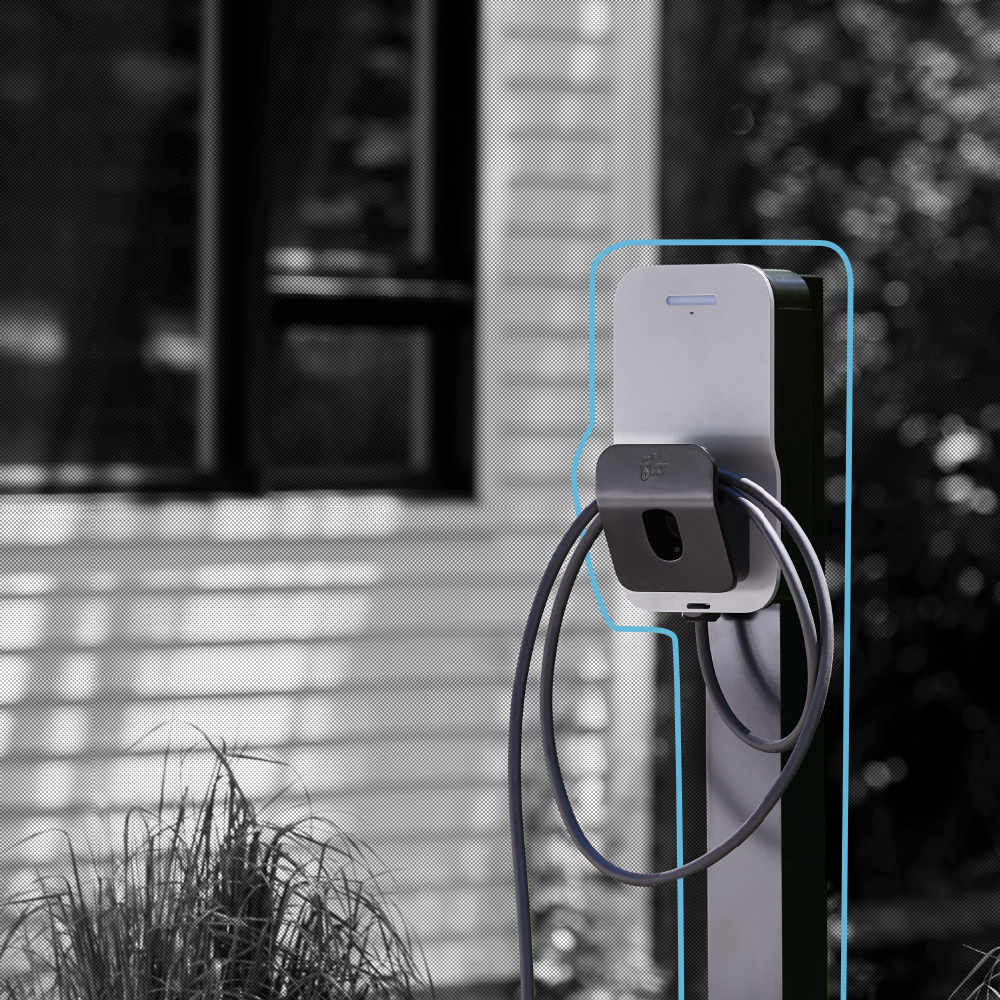
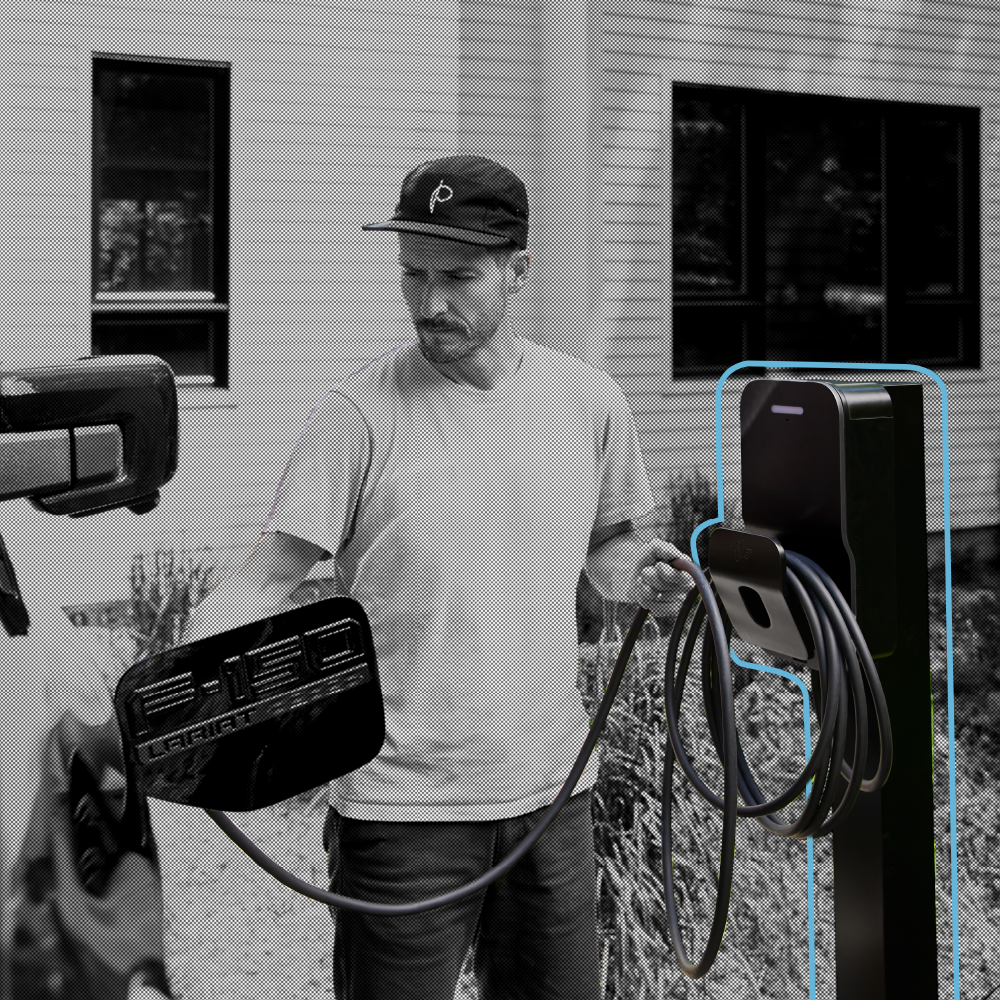
To address the specific challenges presented by the LABSL, FLO’s team of engineers and technicians had to move quickly to adapt their existing technology to the project at hand. The first step was to analyze the SmartTWOTM charging station, and work to understand how it could be grafted directly into the city’s existing street light infrastructure. Ultimately, FLO worked with the city of Los Angeles to develop a mounting bracket which allowed the stations to be installed on the lighting poles. After several iterations and pilot installations, a bracket was developed which suited the purposes of the initial charging station deployment (See Figure 1). Building on this initial success, FLO’s team of engineers developed additional mounting brackets suitable for a variety of street lighting configurations, and further modified the stations with an auxiliary mounting bracket designed specifically for the cable management system of the SmartTWOTM station.
Durability was a key procurement factor for the city of Los Angeles; specifically, the LABSL was intent on finding charging stations that would remain operable through extreme heat or potential vandalism. Similarly, the modular or “hot swap” element of the SmartTWOTM station, which allows a repair technician to quickly and easily replace broken or malfunctioning components in as little as ten minutes, was also an important factor for the LABSL in choosing FLO as a charging solutions provider. This modular technology assists greatly in maintaining a high station “uptime,” a priority for both EV drivers and station owners.
Deploying the chargers quickly was a priority for the city of Los Angeles, and as such the timeline for deployment on this project was condensed. After the initial project approval in August of 2018, a small pilot project was initiated in November of 2018. Shortly after the analytics from the pilot revealed it to be a success, the LABSL placed an inaugural order for 75 SmartTWOTM charging stations; these stations were deployed and active in approximately 90 days, an incredibly condensed timeline as compared to a traditional curbside infrastructure project. A traditional curbside project can take anywhere from 1 to 2 years to deploy, mostly due to design considerations, urban planning and potential construction that was not required in this instance; by leveraging the city’s surplus energy and existing street lighting infrastructure, FLO and the LABSL were able to deploy the initial run of chargers in the city of Los Angeles in under one calendar year.
Los Angeles is a sprawling metropolis covering over 1,300 square kilometres (500 miles), and it was imperative to the city that the SmartTWOTM deployment service the greatest number of potential EV drivers.
Data insights from the deployment’s first year illustrate that the average charging session from these stations added approximately 50.05 kilometres (31.1 miles) of range to the vehicle’s charge, more than satisfying the needs of a commuter in Los Angeles, who travel on-average 20.76 kilometres (12.9 miles) to get to work4.
Additional reports suggest that station uptake has been consistent and trending upward, and these reports also show a 39% average growth rate in gross monthly CO2 savings across the SmartTWOTM stations deployed in Los Angeles.
This charging infrastructure project undertaken by the LABSL represents a strong step forward in the Zero-Emissions Vehicle portion of their Green New Deal, which states that Los Angeles hopes to increase the percentage of electric and zero emission vehicles in the city to 25% by 2025, 80% by 2035, and 100% by 2050. By partnering with FLO, the city of Los Angeles is illustrating what EV charging done right looks like.
A recent system upgrade saw the department transition to an LED energy system, which resulted in excess available power inside the lighting infrastructure. As part of their commitment to fostering EV adoption inside the city’s limits, the city of Los Angeles aspired to using this excess power to install EV charging infrastructure and combat “range anxiety. In detailing their vision for the project, LABSL articulated a specific set of goals and a unique series of challenges. Early conversations with the utility revealed their intentions for the project to be threefold:
- First, to leverage the department’s existing infrastructure (street lighting poles) for installation, thus reducing the overall cost and timeline for deployment
- Second, to source robust and durable hardware capable of functioning in all the diverse neighborhoods the city of Los Angeles offers
- And finally, to deploy the charging stations in a way that would cover a large geographical range, while servicing the largest percentage of the EV driving community possible.
To address the specific challenges presented by the LABSL, FLO’s team of engineers and technicians had to move quickly to adapt their existing technology to the project at hand. The first step was to analyze the SmartTWO™ charging station, and work to understand how it could be grafted directly into the city’s existing street light infrastructure. Ultimately, FLO worked with the city of Los Angeles to develop a mounting bracket which allowed the stations to be installed on the lighting poles. After several iterations and pilot installations, a bracket was developed which suited the purposes of the initial charging station deployment (See Figure 1). Building on this initial success, FLO’s team of engineers developed additional mounting brackets suitable for a variety of street lighting configurations, and further modified the stations with an auxiliary mounting bracket designed specifically for the cable management system of the SmartTWO™ station.
Durability was a key procurement factor for the city of Los Angeles; specifically, the LABSL was intent on finding charging stations that would remain operable through extreme heat or potential vandalism. Similarly, the modular or “hot swap” element of the SmartTWO™ station, which allows a repair technician to quickly and easily replace broken or malfunctioning components in as little as ten minutes, was also an important factor for the LABSL in choosing FLO as a charging solutions provider. This modular technology assists greatly in maintaining a high station “uptime,” a priority for both EV drivers and station owners.
City of Los Angeles
As part of their “Green New Deal”, the city of Los Angeles has committed to transitioning to a more sustainable model of transportation in the immediate future and they partnered with FLO.